
Products
 Geomembrane Welding Machine
Geomembrane Welding Machine
 3D Geonet Composite
3D Geonet Composite
 MDS® Drainage Board
MDS® Drainage Board
 Coated Geosynthetic Clay Liner
Geosynthetic Clay Liner (GCL)
Coated Geosynthetic Clay Liner
Geosynthetic Clay Liner (GCL)
 Smooth HDPE Geomembrane
Smooth HDPE Geomembrane
 Patterned Textured HDPE Geomembrane
Patterned Textured HDPE Geomembrane
 Nitrogen-Explosion Textured Geomembranes
Nitrogen-Explosion Textured Geomembranes
 PVC Geomembranes
PVC Geomembranes
 Multi-Colors HDPE Geomembranes
Multi-Colors HDPE Geomembranes
 LDPE Geomembrane
LDPE Geomembrane
 Spray-Textured Geomembrane
Spray-Textured Geomembrane
 EVA Geomembranes
EVA Geomembranes
 One Fabric One Membrane
One Fabric One Membrane
 Two Fabric One Membrane
Two Fabric One Membrane
 Three Fabric Two Membrane
Spray Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
Three Fabric Two Membrane
Spray Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
土工布.jpg) EPDM Geomembrane
EPDM Geomembrane
 TPO Geomembrane
TPO Geomembrane
 LLDPE Smooth Geomembranes
Nitrogen-Explosion Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
LLDPE Smooth Geomembranes
Nitrogen-Explosion Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
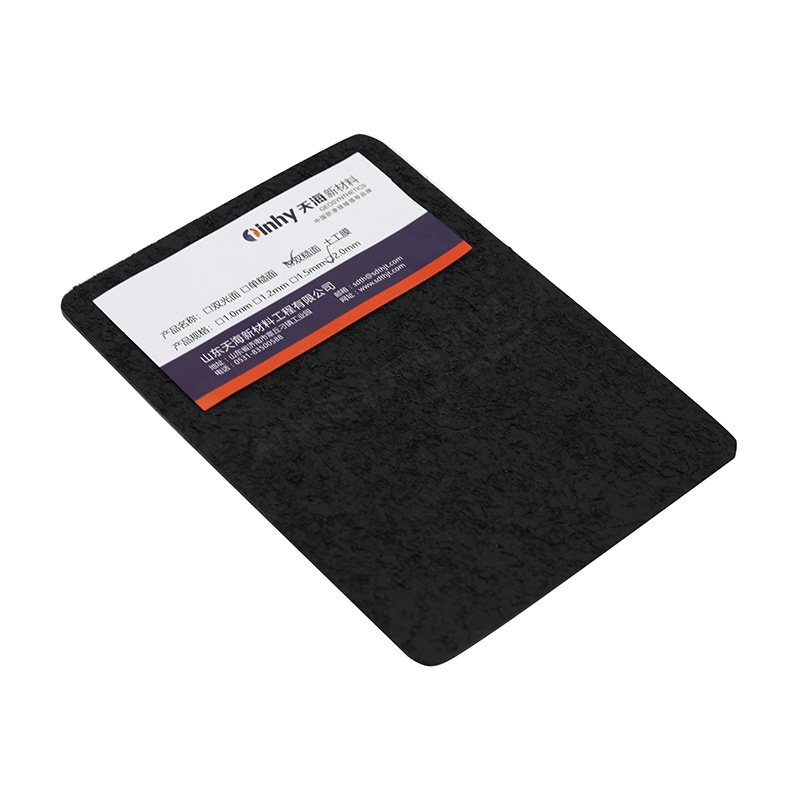 Spray-Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
Spray-Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
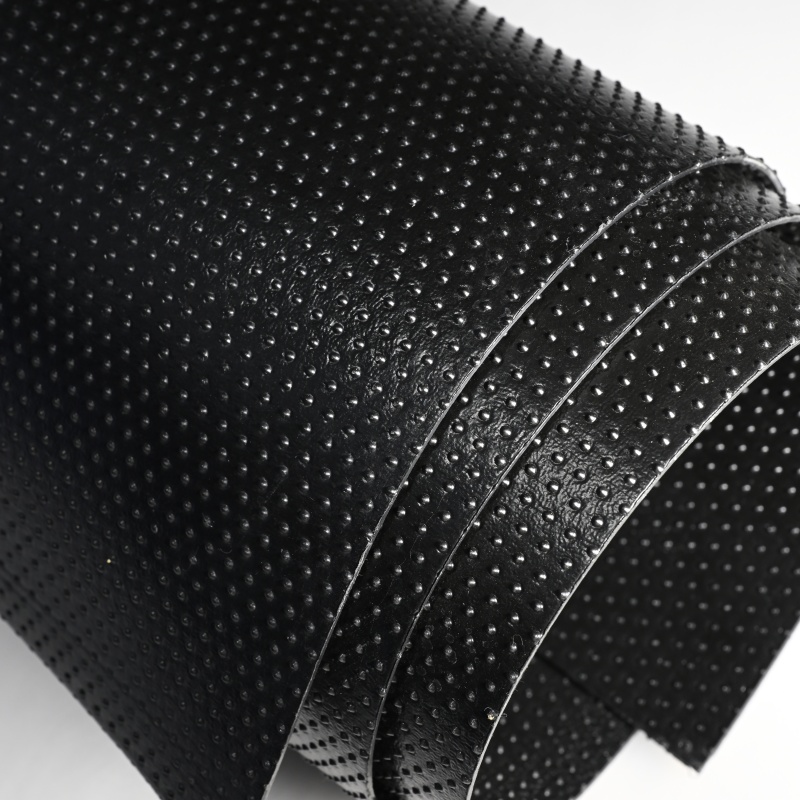 Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
Textured LLDPE Geomembrane
 Polyester(PET) Filament Nonwoven Geotextiles
Polyester(PET) Filament Nonwoven Geotextiles
 Polypropylene(PP) Staple Fiber Needle Punched Nonwoven Geotextiles
Polypropylene(PP) Staple Fiber Needle Punched Nonwoven Geotextiles
 Polypropylene(PP) Woven Geotextiles
Polypropylene(PP) Woven Geotextiles
 Polyester(PET) Staple Fiber Needle Punched Nonwoven Geotextiles
Polyester(PET) Staple Fiber Needle Punched Nonwoven Geotextiles
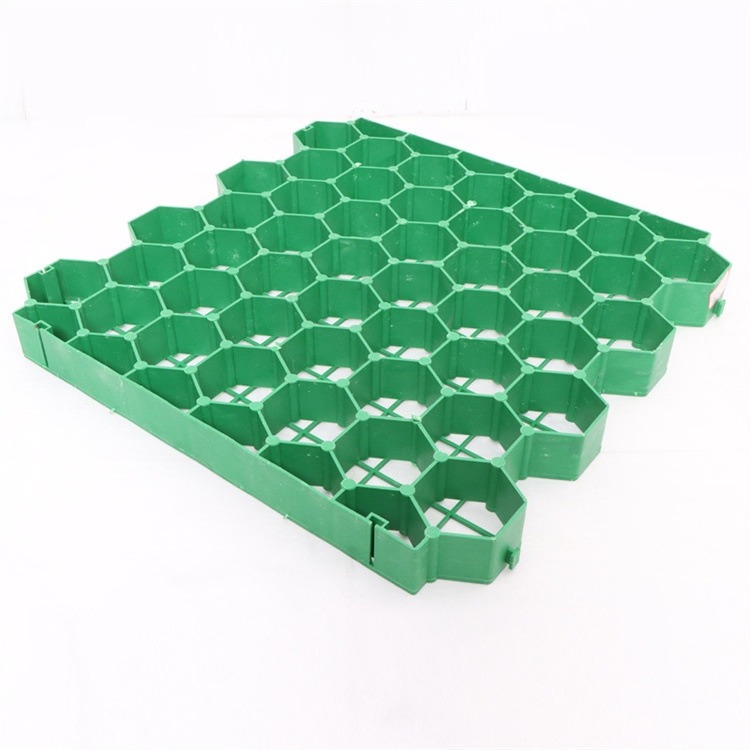 Grass Paver
Grass Paver
 Flexible concrete mat
Flexible concrete mat
 Geogrid
Geogrid
 Geocell
Geocell
 Geomat
Geomat
 Steel Plastic Geogrids
Steel Plastic Geogrids
 Plastic Geogrids
Plastic Geogrids
 Fiberglass Geogrids
Fiberglass Geogrids
 Warp Knitting Polyester Geogrids
Warp Knitting Polyester Geogrids
Geomembranes
Geotextiles
Drainage Materials
Reinforcement & Stabilization Materials
GCLs
Accessories
Other Geosynthetics















土工布.jpg)

















Resources
 Tianhai Conducts Comprehensive Emergency Drill to Strengthen Workplace Safety Defenses
Tianhai Conducts Comprehensive Emergency Drill to Strengthen Workplace Safety Defenses
 Company Mid – Year Summary and Team – Building Activity Report
Company Mid – Year Summary and Team – Building Activity Report
 Is geomembrane a geotechnical engineering material?
Is geomembrane a geotechnical engineering material?
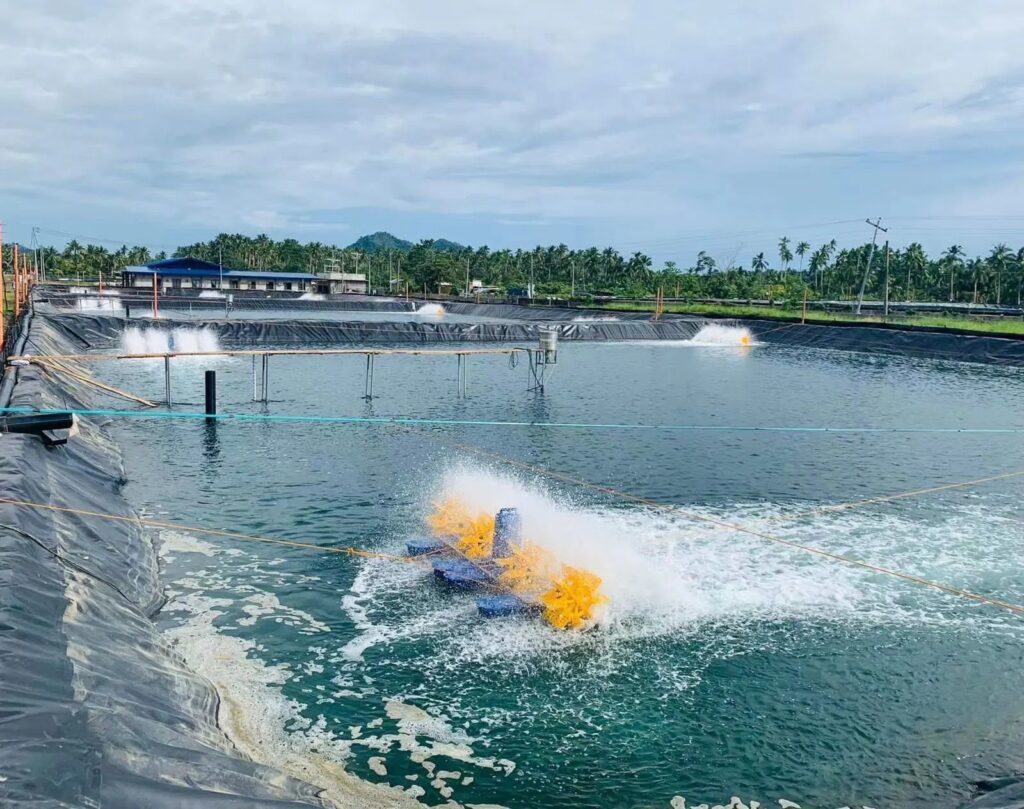 What are the application scenarios of geomembrane?
What are the application scenarios of geomembrane?
 What are the functions of geotextiles?
What are the functions of geotextiles?
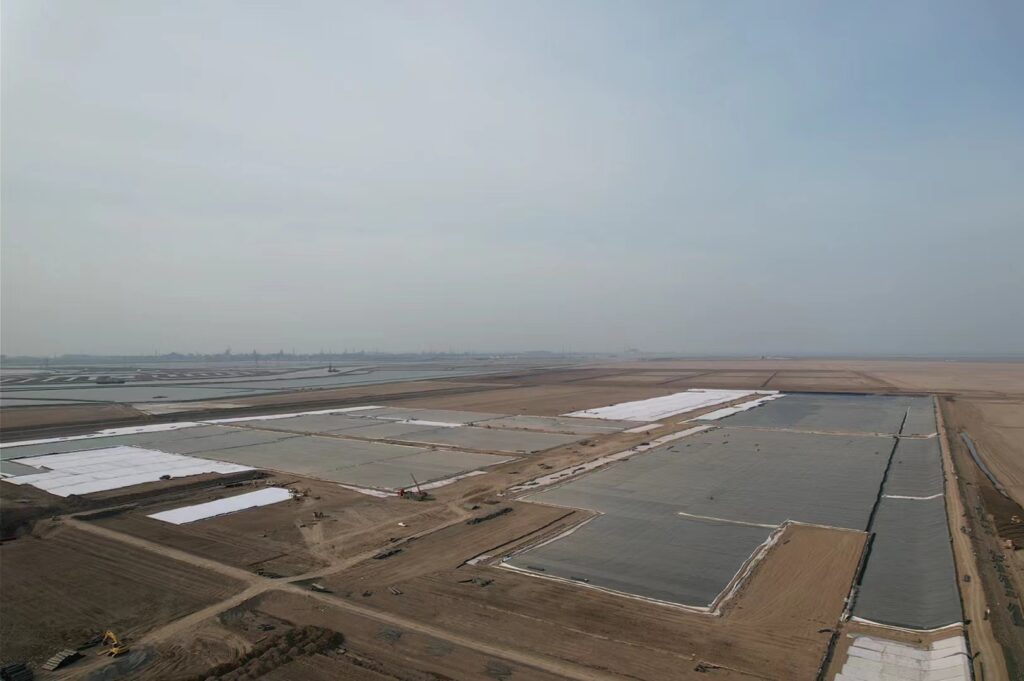 Cómo elegir geomembrana de hdpe en proyectos de ingeniería
Cómo elegir geomembrana de hdpe en proyectos de ingeniería
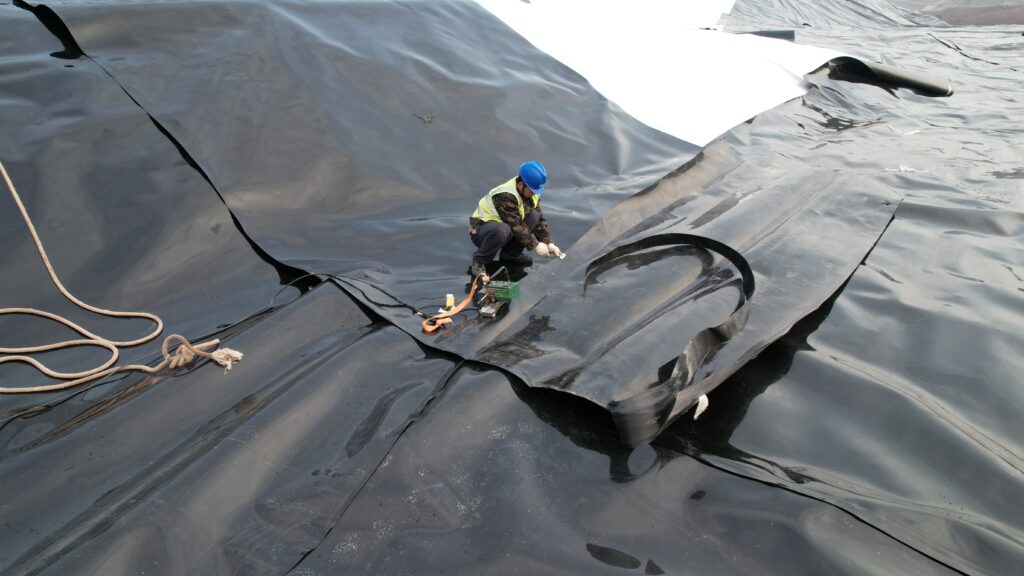 How to choose hdpe geomembrane in engineering projects
How to choose hdpe geomembrane in engineering projects
 ¿Qué ancho elegir para geomembrana?
¿Qué ancho elegir para geomembrana?
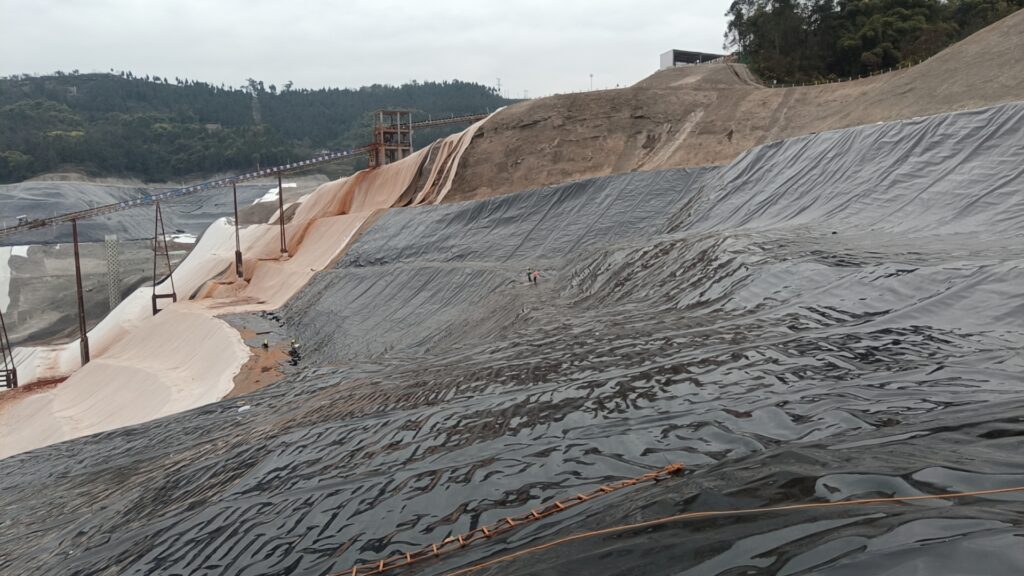 Prueba de envejecimiento térmico de geomembrana.
Prueba de envejecimiento térmico de geomembrana.
 Cinco pasos para la soldadura de geomembranas
Cinco pasos para la soldadura de geomembranas
 China’s Geotechnical Construction Materials Embrace New Opportunities
China’s Geotechnical Construction Materials Embrace New Opportunities
 Tips for Moisture-Proof Storage of Geotextiles
Tips for Moisture-Proof Storage of Geotextiles
 Key Construction Points and Precautions for High-Density Polyethylene Geomembrane
Key Construction Points and Precautions for High-Density Polyethylene Geomembrane
 what is pond lining material ?
what is pond lining material ?
 What is geomembrane?
What is geomembrane?
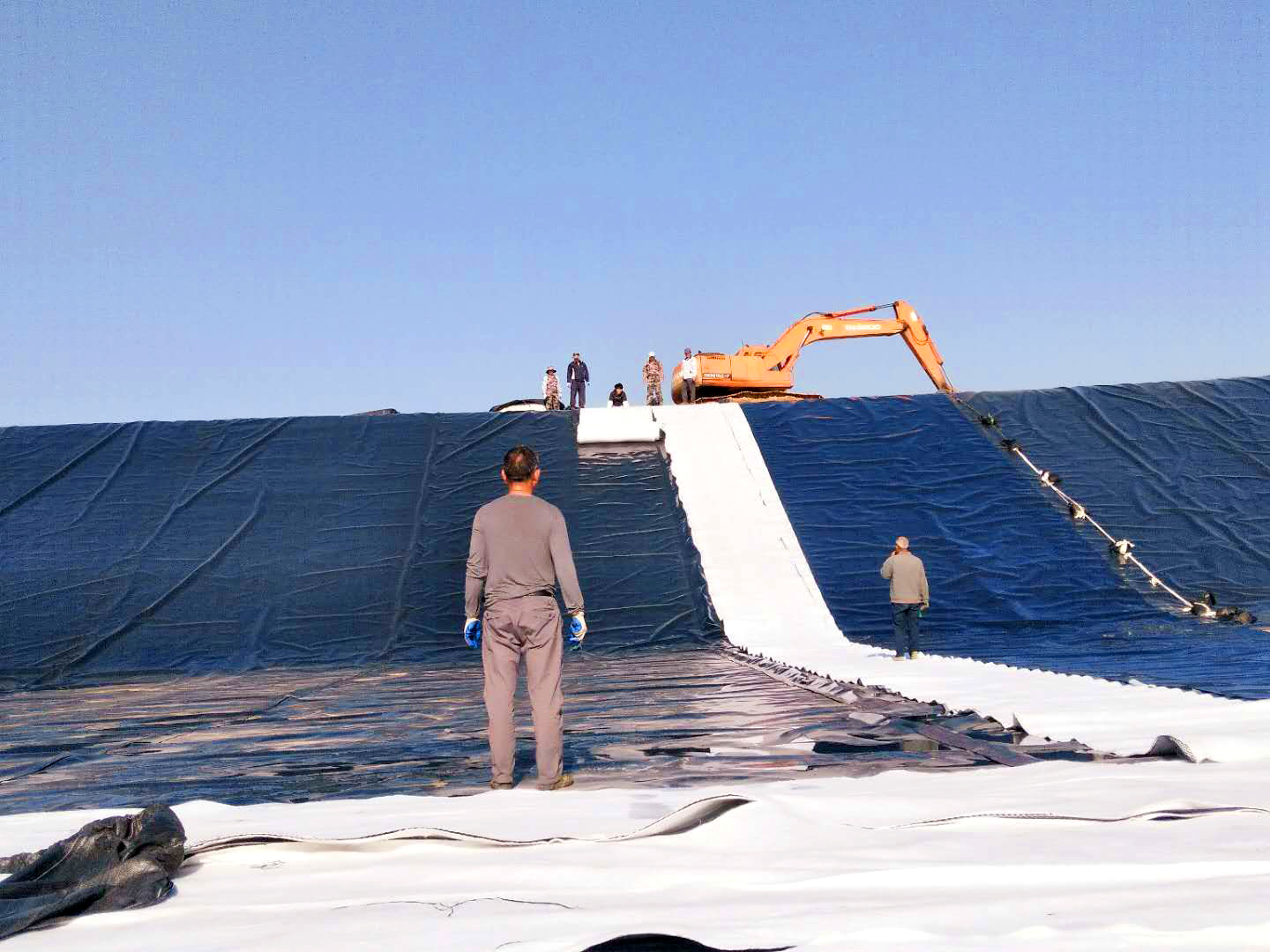 HDPE geomembrane construction plans and technical measures
HDPE geomembrane construction plans and technical measures
 What quality tests do HDPE geomembranes need to do?
What quality tests do HDPE geomembranes need to do?
 Tinhy’s MDS® Drainage Solution
Tinhy’s MDS® Drainage Solution
 Installation Robots
Installation Robots
 Landfill Liner Geomembrane: Tensile Strength and Lifespan Explained
Landfill Liner Geomembrane: Tensile Strength and Lifespan Explained
 What Is 150 GSM Geotextile?
What Is 150 GSM Geotextile?
 What Thickness of Geomembrane Do You Need?
What Thickness of Geomembrane Do You Need?
 What Is the Difference Between Geotextile and Geocell?
What Is the Difference Between Geotextile and Geocell?
 What Is Composite Geomembrane?
What Is Composite Geomembrane?
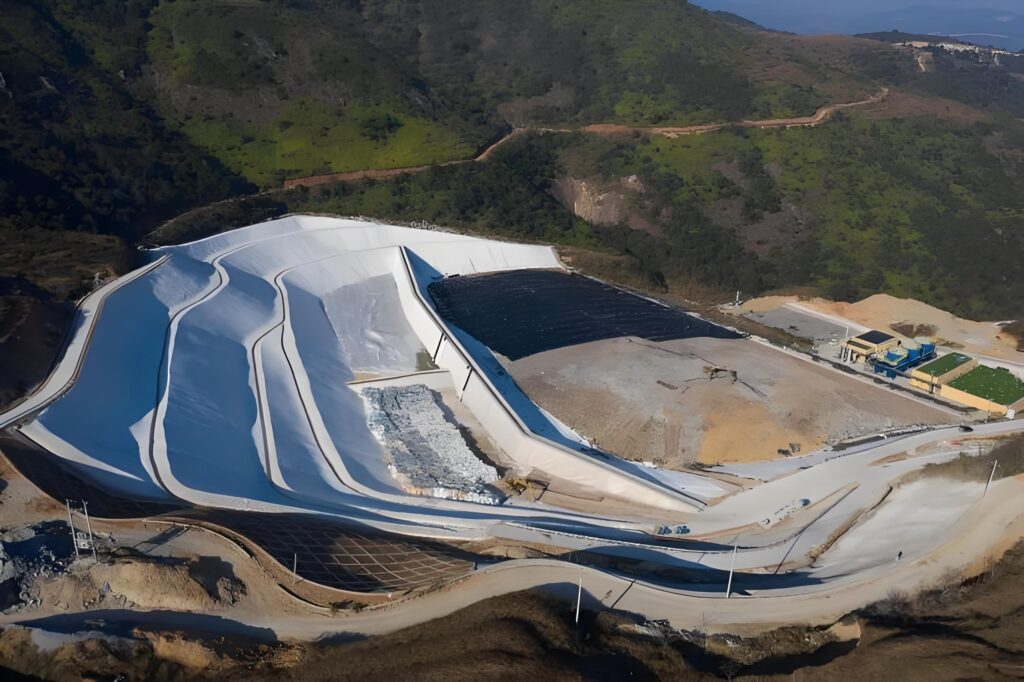 HDPE Liner for Landfill: The Ultimate Containment Solution
HDPE Liner for Landfill: The Ultimate Containment Solution
 What Is High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Pond Liner?
What Is High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Pond Liner?
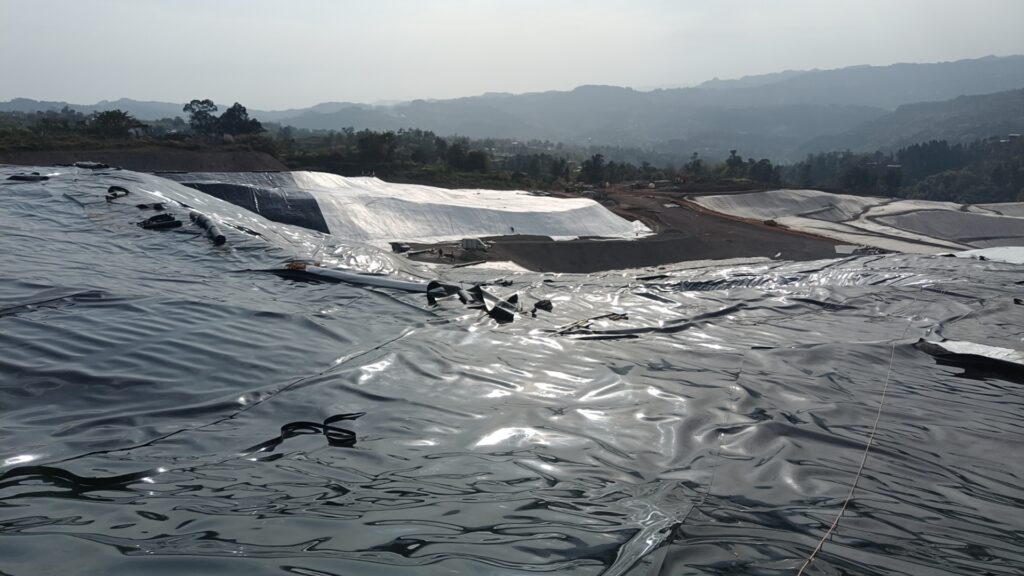 Step To Step Guide To HDPE Liner Installation (Complete Engineering Guide 2026)
Step To Step Guide To HDPE Liner Installation (Complete Engineering Guide 2026)
 Top 10 Geomembrane Manufacturers in the World (2026)
Top 10 Geomembrane Manufacturers in the World (2026)
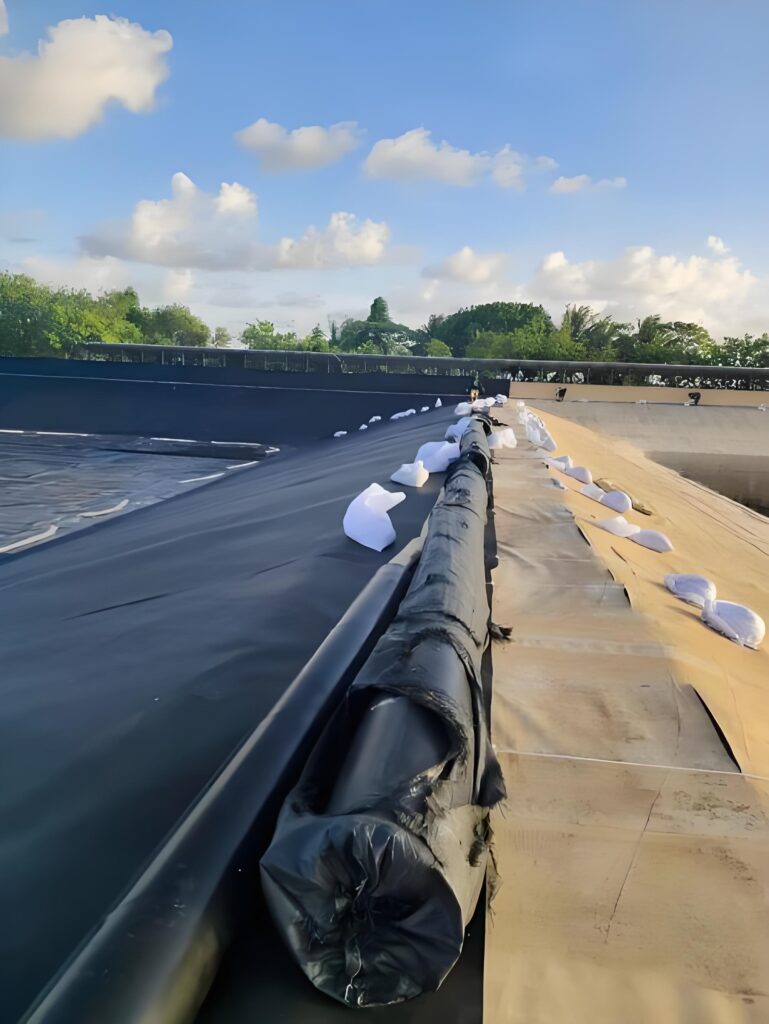 HDPE vs LDPE Pond Liners: Which Is Better for Large Pond Projects?
HDPE vs LDPE Pond Liners: Which Is Better for Large Pond Projects?
 Should HDPE or PVC be used to install geomembrane in reservoirs?
Should HDPE or PVC be used to install geomembrane in reservoirs?
 What is the price of geomembrane?
What is the price of geomembrane?
 Material characteristics of three different geomembranes
Material characteristics of three different geomembranes
 Esquema de construcción de geomembrana de HDPE y medidas técnicas
Esquema de construcción de geomembrana de HDPE y medidas técnicas
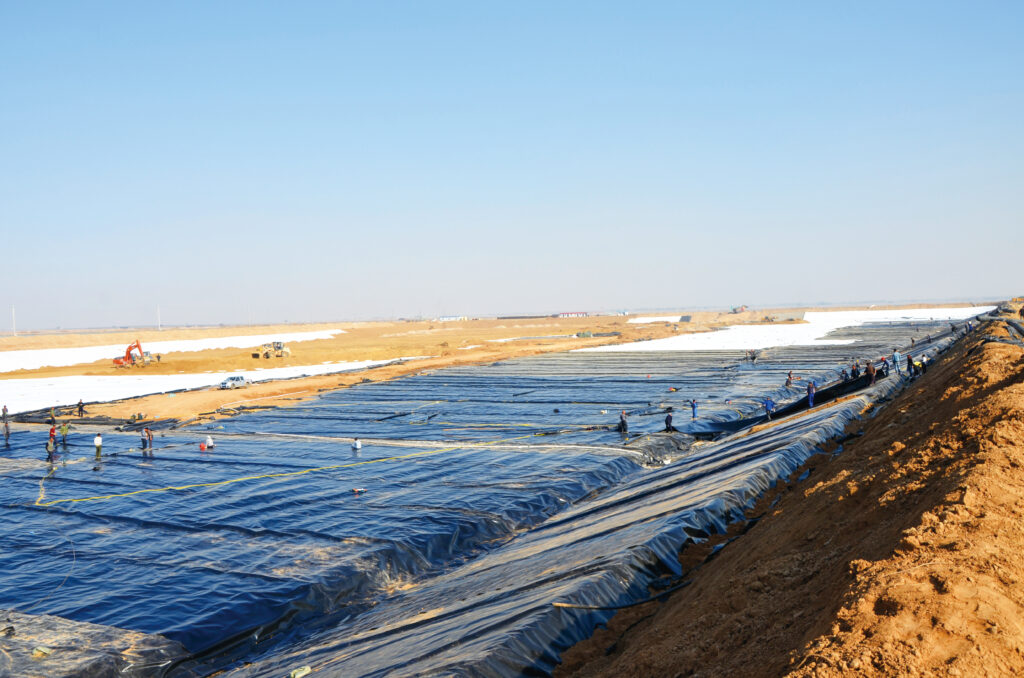 hdpe geomembrane pond liner in Congo (DRC)
hdpe geomembrane pond liner in Congo (DRC)
 How to lay and weld HDPE geomembrane?
How to lay and weld HDPE geomembrane?
 HDPE geomembrane 0.2-4.0mm
HDPE geomembrane 0.2-4.0mm
Company News
Industry News
Knowledge Base
Project Cases
Innovation

















































